Units for measurement
Today we will talk about an important topic related to engineering and that is Units for measurement. Basically units of measure are present in two categories: Imperial Units and Metric units.
What Is the Imperial System?
The British Imperial System was the
official system of weights and measures in the United Kingdom from 1824 until
they adopted the metric system in 1965. The Imperial system standardized
measurements for units like pound and foot that had different meanings in
different places. The United States Customary System is based off British
Imperial units that existed previous to the Weights and Measures Act of 1824.
The basic unit in the Imperial
and U.S. customary systems is the:-
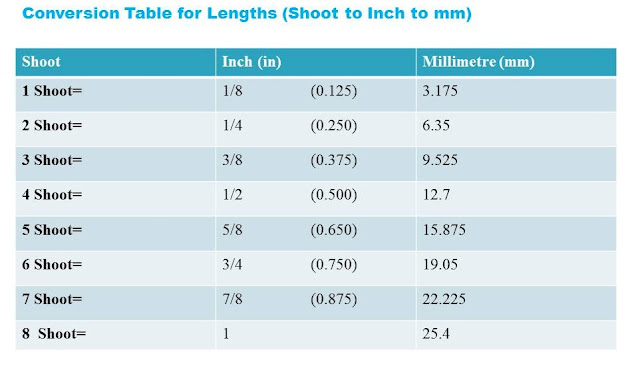
Length= (Inch-in, ft, Yard-yd,
Mile-mi)
We know that the standard unit of
length in imperial system is ‘feet’ which
is written in short as ‘ft.The different units of length are
given here:
What Is the Metric System?
Based on
the meter for length and kilogram for mass, the metric system was first adopted
in France in 1795. After the French Revolution, the government asked scientists
to look into replacing thousands of different traditional measurement systems
with one that could unify the country. The meter was developed by measuring one-ten-millionth
of the quadrant of Earth’s circumference running from the North Pole to the
equator, through Paris. The new unit, equal to about thirty-nine inches, was
called a meter, and all measurements were based upon it.
The
metric system, or SI (Systeme International), is based off this original meter
and currently the official system of measurement for almost all countries,
including the countries of the former British Empire, such as Australia.
(Canada converted to the metric system in the ’70s and ’80s.) The SI
units—fundamental units not based on any other units—are meter, kilogram,
second, ampere (electricity), Kelvin (although Celsius is a more practical
measurement for nonscientific applications), mole (chemistry), and candela
(luminous intensity).
Metric Units
The basic unit in the Metric system
& SI System is the:-
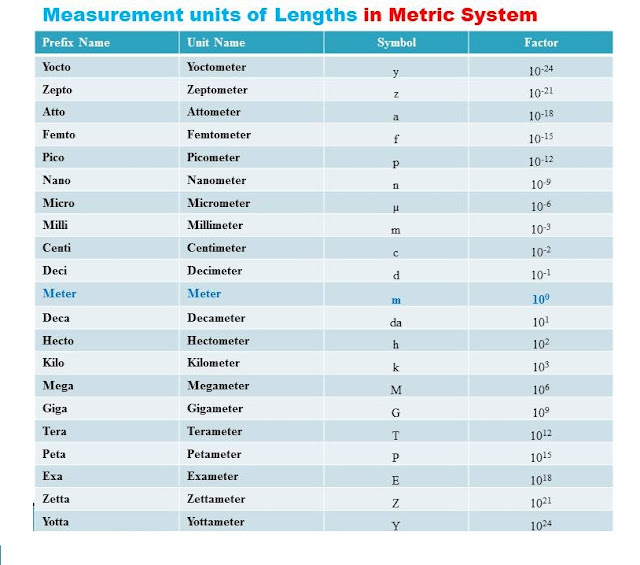
Length= (mm, cm, Meter-m, kilometre-km,
Light Year)
We know that the standard unit of
length is ‘Meter’ which is written in short as ‘m’.





No comments:
Post a Comment